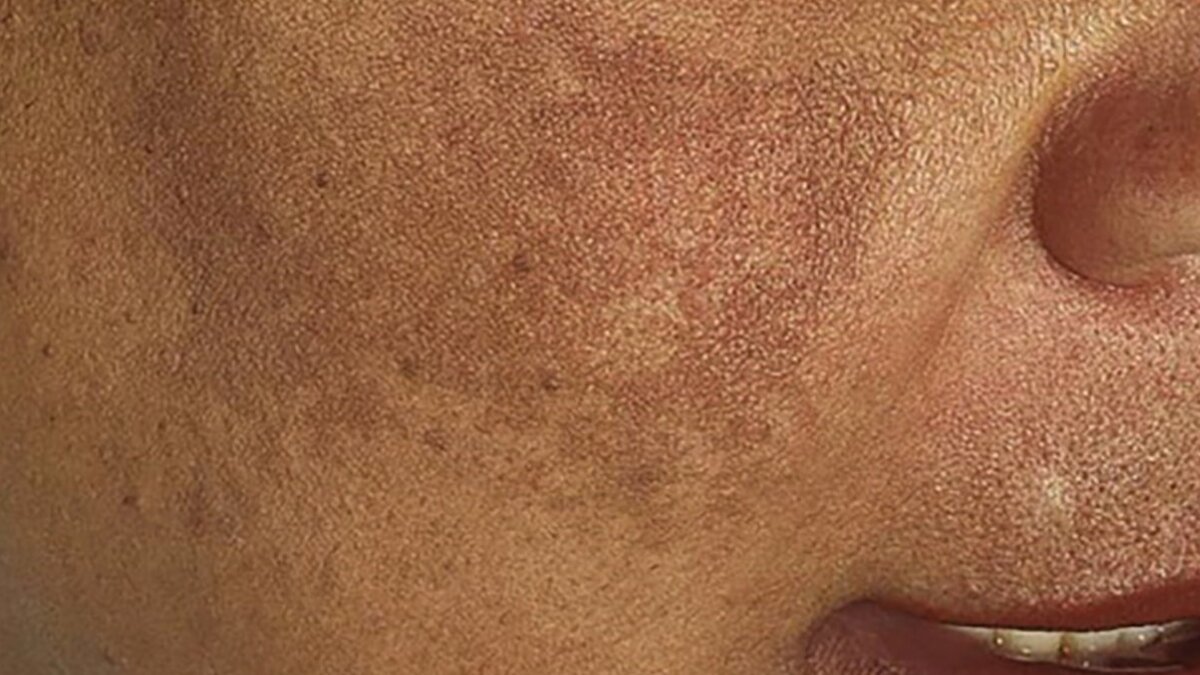
What is dark pigmentation and why it appears on the skin
Dark pigmentation, also known as hyperpigmentation, refers to patches of skin that become darker than the surrounding areas due to an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Melanin is produced by cells called melanocytes, and when these cells become overactive, dark spots can appear.
This condition can affect all skin types and may occur on the face, neck, hands, arms, and other sun-exposed areas. Although pigmentation itself is not dangerous, it can signal underlying issues or be cosmetically concerning for many individuals.
Common causes of skin pigmentation: From sun exposure to hormonal changes
There are several common triggers that lead to increased melanin production and uneven skin tone:
- Excessive sun exposure: UV radiation stimulates melanocytes, leading to sun spots or freckles.
- Hormonal imbalance: Conditions like pregnancy or birth control usage can trigger melasma, especially in women.
- Inflammatory skin conditions: Acne, eczema, or injuries can cause post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation once the skin heals.
- Harsh skincare or cosmetic products: Ingredients that irritate or damage the skin barrier can lead to pigmentation over time.
- Side effects of medications: Certain antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, and antimalarial medications may lead to pigmentation.
- Underlying medical issues: Addison’s disease, hemochromatosis, or vitamin B12 deficiency can also contribute to dark spots.
Each case may have a different underlying cause, making personalized treatment important.
How to prevent dark pigmentation: Dermatologist-backed habits and skin protection
Preventing pigmentation requires daily skin care habits and avoiding common triggers. Dermatologists suggest the following:
1. Daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen
Apply sunscreen with at least SPF 30 every day, regardless of weather or indoor status. Reapply every 2-3 hours if you’re outdoors.
2. Limit sun exposure during peak hours
Avoid being in direct sunlight from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m. Wear hats, scarves, and sunglasses for added protection.
3. Do not pick, squeeze, or scratch the skin
Touching pimples or rashes can worsen inflammation and cause long-term discoloration.
4. Choose gentle skincare products
Avoid products with alcohol, artificial colors, and fragrances. Instead, look for calming ingredients like niacinamide and green tea extract.
5. Maintain skin hydration
Use moisturizers that contain hyaluronic acid or ceramides to strengthen the skin barrier and reduce irritation.
6. Be cautious with new cosmetics
Always do a patch test and check for potential allergens to avoid skin reactions that may lead to pigmentation.
How to treat dark pigmentation on skin: Dermatologist-approved treatments and remedies
Effective treatment depends on the severity, type, and depth of pigmentation. Options include:
Topical creams with active ingredients for pigmentation
- Hydroquinone: A skin-lightening agent used under medical guidance for melasma or dark patches.
- Retinoids (like tretinoin): Speed up skin cell turnover, promoting fading of dark spots over time.
- Vitamin C: An antioxidant that blocks melanin production and helps brighten dull areas.
- Azelaic acid: Useful for both acne and pigmentation, especially for sensitive skin.
- Kojic acid and licorice extract: Natural lightening agents that reduce melanin production.
Chemical peels for skin discoloration
Dermatologists may use peels containing glycolic, salicylic, or lactic acid to exfoliate the top layer and reduce pigmentation. These treatments should be spaced out to avoid irritation.
Laser therapy for deep pigmentation
Laser treatments like Q-switched Nd\:YAG or fractional laser target melanin directly and can show significant improvement in deeper pigmentation like age spots or melasma.
Microneedling and mesotherapy
Microneedling boosts collagen and helps in fading marks by regenerating the skin. In mesotherapy, pigment-lightening substances are delivered directly into the affected area.
Supplements and diet for improving skin tone
- Glutathione: An antioxidant that may reduce melanin when taken regularly.
- Vitamin C and zinc: Boost immunity and skin repair processes.
- Include antioxidant-rich foods like berries, spinach, and green tea in your daily meals.
When to consult a dermatologist for pigmentation issues
Pigmentation often requires professional intervention when:
- The dark patches are spreading, getting darker, or not improving after months of treatment.
- You experience irritation, burning, or peeling from over-the-counter products.
- You’re unsure of the cause, especially if hormonal or health-related factors are suspected.
Early consultation helps to prevent worsening and ensures tailored treatment.